- https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/
- In memory key/value data store
- Extremely fast – improves query turn arounds
- Integrates with CloudWatch
- Runs on EC2 – as a fully managed service
- Cannot access cache via internet or from another EC2. Access only by applications
- EC2s – On-demand or Reserved, but not Spot
- Need do set up security groups and Subnet groups
- Elasticache nodes are run in clusters in a single subnet group but can span multiple subnets in that group
- Clusters have endpoints (URL) – preferred access method over IP
- Caching engines:
§ Memcached – cache, not a DB/ data store, non-persistent
§ Redis – fastest NoSQL, can be used as a data store – persistent
§ In-memory data structure store used as database, cache and message broker. ElastiCache for Redis offers Multi-AZ with Auto-Failover and enhanced robustness.
§ Can’t mix/match caching engines in a cluster – either Memcached or Redis
- Caching techniques:
§ Lazy loading
§ Write through
§ Add TTL
- Non-persistent: Node fails – data lost
- Great as database cache
- Cluster: 1-20 nodes; Max 100 nodes per region
- Integrates with SNS - can send notifications on node failures
- Can scale out – horizontally – by adding nodes to a cluster
- Can scale up – vertically – by switching to a higher-end node type
§ No mechanism to migrate data (unlike on Redis) – the upgraded cluster starts afresh
- No multi-AZ failover. To work around – can manually create Memcached clusters in different AZ and partition the data cross
- Persistent – can be used as DB/data store, not just cache
- Allows for taking of snapshots (manual and automatic into S3)
- Can restore from back up into a cluster
- Can have a primary and read-only replica – with asynchronous replication
- Can’t do read/writes while snapshot is being taken. Best practice – take snapshot from replica
- Snapshots – automated and manual. Delete cluster – automated ones go, manual persist
- To launch a cluster copy in another region:
§ Create snapshot into S3 locally
§ Export snapshot into another region S3
§ Launch cluster from the snapshot in another region
§ This would often be faster than crating an empty cluster and waiting for the application to populate it
- Multi-AZ – can have a read replica in another region
- Shard – collection of 1 to 6 Redis nodes; 1 read/write primary node; 1-5 read replicas; replicas can be in multiple AZs
-
Cluster
mode
§ disabled – one shard max
§ enabled – up to 15 shards (Multi-AZ failover is required and automatically enabled)
- Multi-AZ Failover
§ Detected automatically
§ Most up to date replica is promoted to become Primary
§ Endpoint DNS record is re-pointed to the new IP
§ Other replicas synch from the new primary
§ disabled – one shard max
§ enabled – up to 15 shards (Multi-AZ failover is required and automatically enabled)
- Multi-AZ Failover
§ Detected automatically
§ Most up to date replica is promoted to become Primary
§ Endpoint DNS record is re-pointed to the new IP
§ Other replicas synch from the new primary
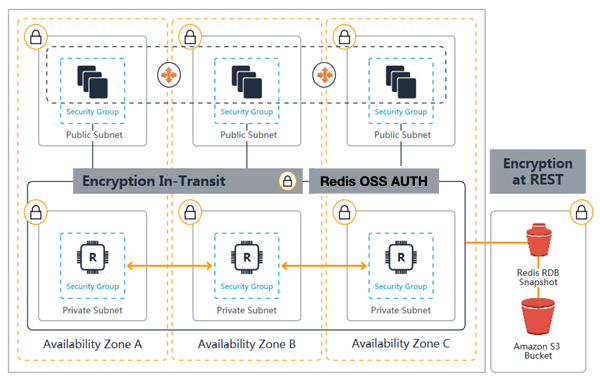
Encrytpion
- ElastiCache for Redis also provides optional encryption features for data on clusters:- In-transit encryption encrypts your data whenever it is moving from one place to another, such as between nodes in your cluster or between your cluster and your application
- At-rest encryption encrypts your on-disk data during sync and backup operations
- Using Redis AUTH command can improve data security by requiring the user to enter a password before they are granted permission to execute Redis commands on a password-protected Redis server- To require that users enter a password on a password-protected Redis server, include the parameter --auth-token with the correct password when you create your replication group or cluster and on all subsequent commands to the replication group or cluster
No comments:
Post a Comment